The new organization setup
If one considers the changing stakeholder expectations, one comes to the conclusion that a functional Insights organization, in which the individual pillars are theme-driven (e.g. Consumer Insights, Market Insights and Brand Insights), is not ideal. This structure is very susceptible to both thinking and acting in silos.
Therefore, different alternatives have been developed to harmonize the classic Insights areas with the new expectations of the stakeholders; the aim being to change from a functional to a process- and stakeholder-oriented organization, and to improve the cooperation of the insights team.
After careful evaluation of various options, opinion-forming and critical discussion, the organizational model in Figure 1 proved to be the most appropriate option. In this approach, an Insights organization is divided into three pillars, which look at Insights from a holistic perspective, and are oriented towards the stakeholder management philosophy. These three pillars are presented in the following section.
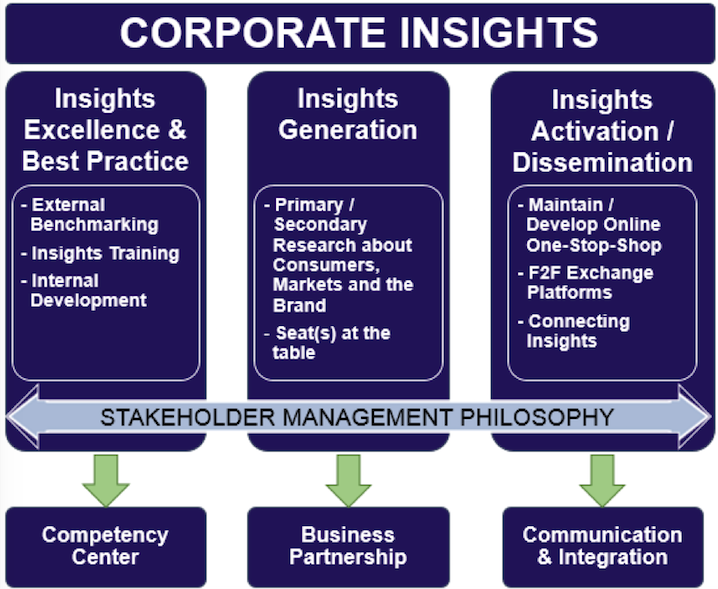
Insights Excellence & Best Practice is an active support function for Insights Generation and takes a proactive perspective. It is about raising awareness of the best practice developed in the Insights industry and ensuring that they are understood and applied where they increase efficiency. Core functions of Insights Excellence & Best Practice are:
- Systematic and ongoing monitoring of the Insights industry to understand which new Insights tools, methods or techniques are being developed.
- Address training needs across the Insights team, and identify suitable providers to cover them in the short to medium term. Secondly, the training of the larger Insights community within the company follows due to the increasing Insights DIY penetration. Especially for association memberships such as ESOMAR, it is essential to adhere to best ethical and standards principles.
- The development and corresponding provision of e-learning modules with content such as “What is an Insight” or “How are Insights generated in the company”.
- Collect and understand the changing needs of different stakeholders within an organization and respond to organizational changes in a timely manner to ensure that stakeholders’ needs can continue to be met.
- Identify development of the current agency portfolio (agency segmentation), e.g. outsourcing opportunities and new partner agencies to generate insights.
- Support for emerging issues such as test store concept, outcome-driven innovation, digital transformation or customer experience design.
- Developing a clear and concise picture of the Insights professional role and communication within the organization.
Insights Generation is the heart of every Insights organization. It ensures the availability of the correct insights at the right time through a meaningful primary and secondary research agenda to support fact-based operational and strategic decision making. In addition, the involvement of the relevant Insights professionals in the right discussions with the right stakeholders must be ensured (seat at the table), e.g. by means of an active agreement. In this context, it is important to have a clear understanding and development path of how team members can become real business partners interacting with stakeholders. Key tasks and responsibilities within Insights Generation include:
- Maintaining
and developing the primary and secondary research agenda.
- Incubator function for basic Insights topics that are still missing.
- Ensure visibility and points of contact between top and senior management (insights sponsorship, engagement, decision making) and middle/lower management (insights users).
- Introduction of stakeholder segmentation based on different models of collaboration to ensure a differentiated approach to service delivery. Not every stakeholder / every project justifies or needs a full-service approach.
- Ensuring continuous collaboration with Insights Excellence & Best Practice and Insights Activation & Dissemination.
- Implementation of a holistic approach to data analysis: Combination and triangulation of different sources from different areas.
Insights Activation & Dissemination plays a key role in: 1) disseminating existing knowledge in order to make it accessible and transparent, 2) supporting important stakeholders in making the best use of this existing knowledge, and 3) linking different insights. The priorities are:
- Ensuring
a consistent, holistic data approach by creating synergies between the
different Insights topics (e.g. brand and shopper)
- Support Insights Generation in the initial and final stages of new initiatives.
- Integration and networking of relevant target groups (exchange platform, topic/target, participants) through appropriate stakeholder segmentation.
- Creation of an intranet-based online solution where the relevant insights can be accessed and used by internal stakeholders. Individualizations, powerful search functions or the linking of different insights are important success factors.
- In addition to the intranet-based online solution, F2F platforms are necessary to complement this offering. There, employees can exchange information, close knowledge gaps and receive impulses for the activation of insights. Interpersonal interaction in the field of knowledge transfer is crucial via platforms such as regular Insights Alignment Meetings, “Lunch and Learn’s” or Workshops.
- While individual subject areas contain valuable insights as independent Insights studies, there is further potential in linking these studies. “Connecting the dots” in the Insights section will become even more important in the future. In this way, additional insights can be generated without commissioning further primary research. This is also an effective advertising tool for Insights departments to demonstrate the added value of Insights for the business, as known from case studies of consulting firms.
Findings and practical suggestions
One challenge lies in the size of the organization in that sense that it has too many employees. The solution depends on the company specific Insights philosophy: If everything is done internally, then the challenge seems justified. However, if trusted external research agencies are developed into real partners – working together in the medium to long term, and not only on limited ad-hoc projects, – and standard processes can be outsourced to research agencies that act as an extended arm of the internal insights department, such partnerships allow companies to keep their insights structures relatively lean.
By applying this new organizational model, companies can expect a number of improvements from the Insights department. Here are the most important ones:
- The
quality of insights gained increases as the team members who are responsible
for the Insights generation can fully concentrate on generating insights and do
not have to deal with additional issues related to Insights Excellence &
Best Practice or Insights Activation & Dissemination.
- The attractiveness of the Insights department as an employer increases – for existing team members, but also for other employees in the company. The new and broader competencies required in the three pillars go beyond the pure Insights competencies.
- The cooperation and exchange between the three pillars improves and new ideas for the further development and improvement of the Insights department emerge.
- Stakeholders benefit from higher quality due to the four-eyes principle, as approaches and topics are first critically discussed and examined within the Insights department before something sub-optimal is delivered to the stakeholders.


